ALBUM – View my German East Africa album
Fast Facts
Region: Eastern Africa
Group: German Colony
Classification: Colony
Prior Regime: Tribal Populations
Key Dates:
1884 – German Protectorate formed, administered by the German East Africa Company
1891, Jan 1 – Germany assumed control from the Charter company and formed the German East Africa Colony
1905 – 1907 – Maji Maji Uprising
1916 – Allied powers assume control of the Colony
1919 – Colony was divided between Britain and Belgium
Following Regime: Tanganyika (Britian) and Ruanda-Urundi (Belgium) and the Kionga Triangle (Mozambique)
Scott Catalogue: (German East Africa) 1-41
Pick Catalogue: (German East Africa) P1-49, R
History

Germany immediately began launching its own expeditions, and quickly claimed various territories in Africa and the Pacific. With Germany joining the “Scramble for Africa”, great concern rose among other European Powers, especially Britain and France. King Leopold I of Belgium urged France and Germany that an agreement needed to be worked out, which eventually resulted in the convening of the Berlin Conference in November, 1884. At the conference, the the major European colonial powers carved up Africa for colonization, thus, with the exception of Ethiopia and Liberia, all of continent was to be ruled by the Europeans.
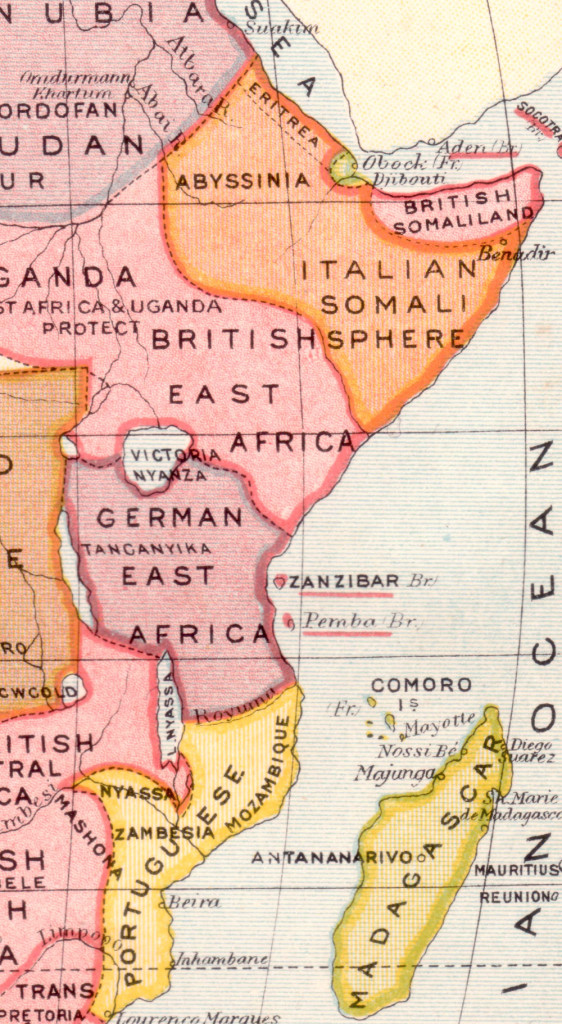
From this agreement, German East Africa Protectorate (today Tanzania, Burundi and Rwanda) was established. Initially, the territory was administered by charter to the Deutsche Ostafrikanische Gesellschaft (German East African Company).
From the beginning, the German East African Company struggled to maintain order, as the local population strongly resisted colonization. Constant revolts and battles took place requiring intervention from the German military. Eventually it became apparent that the German East African Company could not hold the territory without constant support from the German military. On 1 Jan, 1891, Germany ended company control by buying back the charter and establishing the Deutsch Ostafrika (German East Africa) Colony.
Rebellions continued to be frequent among the native population. One of the more significant was the Maji Maji Uprising. In 1905, Kinjikitile Ngwale, a local tribal prophet, claimed that a sacred water source called “Maji Maji could repel German bullets. The locals, armed with spears and arrows doused in the water, began attacking German outposts and destroying crops. As the rebellion spread across the country, German retaliation was brutal. By the end of the rebellion in 1907, over 75,000 natives were dead.
As World War I broke out, Africa was an important theater of conflict between the various colonial armies. Some of the earliest battles occurred in German East Africa with Belgian forces attacking from the west, British forces from the south and Indian forces from the east. An allied blockade of Dar es Salaam created major shortages in the colony. Most of the solders consisted of Africans commanded by European officers, however by 1917, the allies controlled most of German East Africa. At the end of the war, the German Colony was split up: Tanganyika was mandated to the British, Ruanda-Urundi was mandated to the Belgians, and the small area of the Kionga Triangle became part if Mozambique.
Stamps
 ALBUM
ALBUM
The first stamps were issued in German East Africa in 1893 when colonial authorities surcharged German stamps in East African Rupees: (64 Pesa = 1 Rupee). Indian Rupees were the primary currency of trade routes in the region.
In 1896, new stamps were issued, also surcharged on German stamps. The new issues were overprinted diagonally and included the name of the colony: “Deutsch-Ostafrika”.
Beginning late 1900, all German colonies began issuing stamps with a common design, featuring the “Hohenzollern”, the personal yacht of the German Kaiser. The stamps came in two sizes and used a key plate process, where the top and bottom scrolls were left blank, and individual colony names and values would be added as needed.
The yacht stamps of German East Africa were first issued on 1 January, 1901. These stamps were used until 1905, when Germany assumed responsibility for currency in the Colony. The official monetary unit was changed to the “heller” replacing the “pesa” (100 heller = 1 rupee.) With this change, new stamps were issued.
For all of the early issues, stamps of German East Africa were printed on paper without a watermark, however beginning in 1906, the yacht stamps began to be resupplied on paper with a lozenge watermark. Stamps continued to be printed even after most of the territory was occupied by the British and Belgians in 1916.
Banknotes
In 1905, German East Africa issued a series of 5 banknotes in denominations of 5, 10, 50, 50, and 100 Rupees (Rupien). A 500 Rupee note was issued in 1912.
During war, German East Africa was blockaded, therefore crude emergency notes were printed in Dar es Salaam between 1915-1917. There are many varieties of the notes printed on whatever paper was available.
Links
German East Africa from Wikipedia
VIDEO – Berlin Conference 1885
VIDEO – How the Europeans Divided Africa
German East Africa Postage Stamps from Stamp Collecting World
German East Africa Postmarks from Stamp Collecting World
German East Africa from Big Blue 1840-1940
German East Africa Currency from ATS
A Monetary History of German East Africa by John E. Sandrock
Banknote Gallery of German East Africa at RealBanknotes.com